Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH) is the presence of an enlarged prostate gland, a condition which is more prevalent in older men. Men who suffer from BPH experience many of the same symptoms as prostate cancer; however, BPH is non-cancerous and the presence of this condition does not mean that a man is more likely to develop prostate cancer in the future.
What is Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)?
Although BPH is common in older men, many may still ask “What is BPH (benign prostatic hypertrophy)?”
BPH is the inflammation or enlargement of the prostate gland. The risk for developing BPH increases with age, because as men get older, their prostate enlarges. The reason behind this is attributed to changes in hormone levels. As men get older, the amount of active testosterone in the blood drops, resulting in a higher proportion of estrogen, which is suggested to promote cell growth in the prostate gland and lead to prostate enlargement.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), BPH is prevalent in more than 50% of men over age 60 years and in around 90% of men over the age of 70 years.
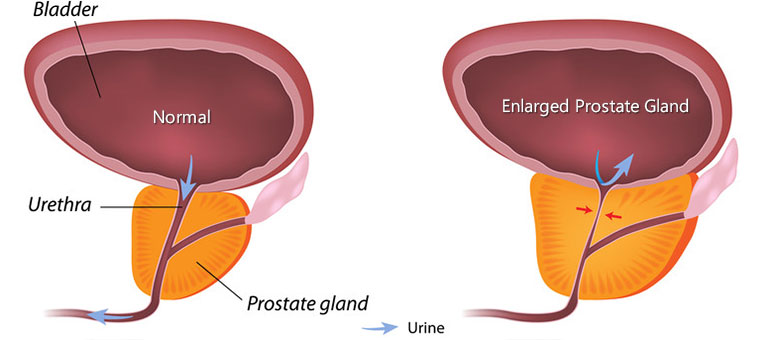
Location of Prostate Glands and Relationship to BPH Symptoms
The prostate gland is located behind the rectum and below the bladder. This gland surrounds the urethra, which is the thin tube that carries blood from the bladder to the outside of the body. The main function of the prostate gland is to help produce semen, which is also transported from the body during ejaculation via the urethra in men.
When the prostate gland is enlarged by a condition, such as BPH, it impinges on the bodily functions in that region. As such, BPH symptoms include many urinary-related symptoms that are also often seen in men who have prostate cancer.
BPH Symptoms and Warning Signs of Enlarged Prostate
The most common BPH symptoms are problems associated with urinating, as the enlarged prostate pushes on the urethra and bladder. BPH symptoms include the following:
- difficultly beginning to urinate
- a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
- waking up multiple times in the night in order to urinate
- the sudden urge to urinate
- frequent urination
- pain when urinating
If the bladder does not completely empty, a urinary tract infection can occur. Some men may also experience blood in their urine, which occurs becuase blood vessel are broken on the inner surface of the enlarged prostate or a sudden streching of the bladder.
How to Distinguish BPH Symptoms from Prostate Cancer
While men who suffer from BPH experience many of the same symptoms as prostate cancer, BPH is non-cancerous and the presence of this condition does not mean that a man is more likely to develop prostate cancer in the future. However, a man who is experiencing BPH symptoms must first undergo some screening tests, such as a PSA test and DRE (digital rectal examination), in order to rule out the presence of prostate cancer. As such, any man who experiences BPH should seek help from their doctor.
While one-third of all mild cases of BPH can be resolved without any treatment at all, when a man in inconvenienced by his BPH symptoms or the condition is posing a problem to his health, pharmacological drug therapy can be employed, with surgery reserved for more severe BPH cases.